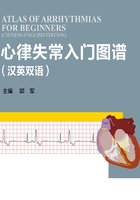
5)ECG parameter measurement (Fig.1-13) 心电图参数测量(图1-13)

Fig.1-13 Normal ECG waves and intervals
图1-3 正常心电图波形及间期
P wave
Sequential depolarization of the right and left atria and it represents atrial activation. Normally,P wave is usually upright in Ⅰ , Ⅱ , and aVF, negative in aVR, and variable in Ⅲ , aVL.
a) Duration < 0.12s
b) Voltage<0.25mV
c) Frontal plane P wave axis: 0° to +75°
P波
左右心房的顺序除极,代表左右心房的激动。通常P波在Ⅰ、Ⅱ和aVF导联主波向上,aVR导联主波向下,在Ⅲ、aVL导联上方向不确定。
a) 时间:<0.12s
b) 电压:<0.25mV
c) 电轴方向:0°~+75°
P-R interval
It is measured from the beginning of P wave to the beginning of QRS complex in the frontal plane, and represents time required for a supraventricular impulse to depolarize the atria, traverse the AV node, and activate the ventricle. Normally P-R interval is 0.12 to 0.20 seconds. If P-R interval is longer than 0.20 seconds, first degree AV block should be considered.
P-R间期
P波起点到QRS波群开始的时间,即激动从心房途经房室结传至心室的时间。正常成人P-R间期0.12~0.20s,大于0.20s时考虑一度房室传导阻滞。
QRS complex
The normal QRS complex represents the simultaneous activation of the right and left ventricles.The first downward wave is the Q wave, and the first upward wave after the Q wave is the R wave,then the downward wave after the R wave is the S wave. Normal QRS duration is shorter than 0.11 seconds. Small r waves begin in V1 or V2 and increase in size up to V5 in precordial leads. The RV6 is usually smaller than RV5. In V3 or V4, the amplitude of R wave is about the same as S wave.
QRS波群
即心室除极波。第一个向下的波为Q波,继Q波之后第一向上的波为R波,R波后向下的波为S波。正常成人QRS时间<0.11s。胸导联上V1、V2导联QRS波群的形态通常是小r波,从V1至V5导联R波和S波的比例逐渐增大,V6的R波通常小于V5导联。而典型的移行点在V3或V4导联R波振幅与S波振幅大致相等。
ST segment
The isoelectric segment is from the end of the QRS complex to the beginning of the T wave,representing phase 2 (the plateau) of the myocardialaction potentials. It represents the time from depolarization to preceding ventricular repolarization. Depression of the ST segment by 0.05mV from the baseline is abnormal and elevation of the ST segment by 0.1mV from the baseline is abnormal,except V1-V3.
ST段
QRS波群终点至T波起点间的等电位线,反映心室复极的2相平台期。代表心室除极完毕到复极开始的一段时间。ST段在任何导联压低不应超过0.05mV,抬高不应超过0.1mV(V1~V3导联除外)。
T wave
The T wave represents ventricular repolarization. The direction of normal T wave is consistent with QRS wave. T wave in Ⅰ , Ⅱ , V4-V6 leads is usually upright. T wave in aVR lead is usually inverted. T wave in Ⅲ, aVL, aVF, V1-V3 lead might be upright or inverted or bidirectional. If T wave in V1 lead is upright, then that in V2~V6 lead should not be inverted.
T波
心室复极波。正常T波方向与QRS波主波方向一致。T波方向在Ⅰ、Ⅱ、V4~V6导联向上,aVR导联向下,Ⅲ、aVL、aVF、V1~V3导联可以向上、向下或双向。如V1导联的T波方向朝上,则V2~V6导联就不应该朝下。
QT interval
It is from the beginning of QRS complex to the end of T wave. It represents the time of ventricular depolarization and repolarization. QT interval is usually 0.32s to 0.44s in normal heart rate.
QT间期
QRS波群起点至T波终点时间,代表心室除极和复极的总共时间。其随心率变化而变化,正常心率范围内QT间期在0.32~0.44s。
U wave
It is the low and flat wave at 0.02-0.04s after T wave, which direction is consistent with T wave.Normally it’s not obvious.
U波
在T波后0.02~0.04秒出现的低平波,方向与T波一致。正常心电图U波不明显。
Parameter measurement 参数测量
The most basic measurement parameters include heart rate (HR), P wave duration, P-R (PQ) interval, QRS complex duration, Q-T / Q-Tc / QTd interval, average P, R, T axis, and so on.Millivolts (mV) is the unit of amplitude, and it can be replaced by millimeter (mm) in special cases,represented with 10mm/mV. A standard ECG is printed at 25mm per second or 25 small squares per second. The duration of individual waves can be calculated.
最基本的测量参数包括心率、P波时限、P-R(P-Q)间期、QRS时限、Q-T/Q-Tc/QTd间期、平均P、R、T电轴等。测量振幅单位用毫伏(mV)表示,特殊情况下可以用毫米(mm),用10mm/mV表示。标准的心电图通常走纸速度为25mm/s或25小格/秒,此时可计算各波形时限。
Standardization of ECG measurement (Fig.1-14)
At present, single-channel ECG machines are still used by the majority of domestic medical institutions. To trace an electrocardiogram, we always switch 12 leads manually. The analysis of ECG parameters measured by just one lead is outdating, and also has certain deviations compared with the actual situation. It is not optimal to achieve standardization ECG measurement by this way. Therefore the production and use of single-channel ECG machines should be replaced by synchronous 12-leads ECG machines gradually.
心电图的标准化测量(图1-14)
目前国内绝大多数医疗单位所使用的心电图机仍是单通道心电图。描记一份心电图,需要切换12次导联。只能在一个导联上进行心电图的参数测量分析,这种落后的心电图机描记出的心电图,测量出的各项参数与实际情况有一定偏差。此种方式不可能实现心电图测量标准化,因此推荐逐渐替换为十二导联同步心电图。

Fig.1-14 Measurement of single-lead ECG
图1-14 单导心电图的测量方法
The P wave duration:It is from the origination to the end point in the inner edge of P wave.
P-R interval: It is from the starting point of P wave to the starting point of QRS.
QRS duration: It is from the starting point of Q wave to the end point of R (s) wave.
Q-T interval: It is from the QRS starting point to the end of T wave. The single-lead ECG can only be completed on the same lead.
测量P波时限:自P波起始内缘测量至P波终点内缘。
测量P-R间期:自P波起点测量至QRS起点。
测量QRS时限:自Q波起点测量至R(s)波终点。
测量Q-T间期:自QRS起点测量至T波终点。单导描记心电图只能在同一个导联上进行测量。
Measure time 时间测量
P wave duration
The P wave duration may be not same in different leads, and it’s more accurate if measured by synchronous 12-leads or the quadrature ECG. As the spatial P ring was parallel to the frontal plane, the P wave in limb leads is clearer than the chest leads. P wave duration should be measured from the starting point of the earliest P wave to the end point of the latest P wave. The widest P wave should be selected form easurement in 12 leads.
P波时限
P波时限在不同导联可有不同,在12导联同步记录的心电图上或正交心电图上进行测量比较精确。由于空间P环平行于额面,肢体导联P波比胸导联P波清晰。从最早P波的起点测量至最晚的P波终点的间距为P波时限,应选择12导联中最宽的P波作为P波时限。
P-R interval
P-R interval can be variable in different leads. The accurate P-R interval should be measured from the earliest P wave to the earliest QRS starting point in the 12-lead synchronous recording.It is recommended to use a combination of X, Y, Z leads or similar orthogonal bodies in 3-lead electrocardiographs such as Ⅰ , aVF, V1; Ⅲ , aVR, V2; Ⅲ , V1, V4 or Ⅰ , Ⅱ , Ⅲ leads. P-R intervals should be recorded in a lead of single-channel ECG including wide P wave and Q wave.
P-R间期
P-R间期在各个导联上可有不同,精确测量P-R间期应是在同步记录的12导联中最早的P波起点至最早的QRS起点的间距。如使用3导联心电图仪器,建议采用X、Y、Z导联或类似正交体的组合导联,如Ⅰ、aVF、V1,Ⅲ、aVR、V2或Ⅲ、V1、V4测量分析,也可在Ⅰ、Ⅱ、Ⅲ导联上测量。单通道描记的心电图,应选择P波宽大,又有Q波的导联进行测量。
QRS intervals
Correct measurements should be made in 12-lead synchronized ECG, from the starting point of the earliest QRS to the endpoint of the latest QRS. The diagnostic criterion for Q wave in myocardial infarction is based on single-channel ECG. Thus, equipotential line may be included in abnormal Q waves and narrow the Q wave width. The ECG Standardization Working Group of European Community recommends that the original Q wave measurement definition (excluding the equipotential time) are not abandoned until the new diagnostic criteria are established. The widest QRS in 12 leads of single channel ECG should be selected for measurement.
QRS时限
正确测量应在12导联同步心电图记录中进行。最早的QRS起点至最晚的QRS终点的间距为实测QRS时限。心肌梗死Q波的诊断标准是建立在单导心电图基础上的。因此,某些导联异常Q波的时间可能包括了一段等电位线,而使Q波宽度变窄。欧共体心电图标准化工作小组建议在新的诊断标准建立之前,仍可沿用原来的Q波测量定义(不包括等电位段时间)。单通道心电图,应选择12导联中最宽的QRS进行测量。
Q-T interval / QTd time
Q-T interval is measured from the earliest QRS starting point to the latest T wave end point in 12-lead synchronous ECG. In the single lead, V2 or V3 is recommended for measurement. We should record the longest Q-T interval, excluding U wave. Q-Td: the longest Q-T interval minus the shortest Q-T interval, and its unit is millisecond(ms).
Q-T间期/QTd时间
12导联同步记录的心电图中最早的QRS起点至最晚的T波终点的时距为Q-T间期。在单导联,推荐的测量导联是V2或V3,取其中最长的Q-T间期,Q-T间期不能把U波计算在内。Q-Td:最长Q-T间期减去最短Q-T间期,时间单位用ms表示。
Amplitude measurement 振幅测量
P wave
We should record the P wave amplitude in a lead with the highest amplitude of P wave. The horizontal line before the starting of P wave is used as reference. The forward P wave is measured vertically from the edge of the P wave basis to the peak, and the negative P wave is measured from the P wave baseline to the bottom of the wave vertically.
P波
选择P波振幅最大的导联测量P波振幅,P波振幅测量以P波起始前的水平线为参考,正向P波振幅自P波基线上缘垂直地测量到波顶点,负向P波振幅自P波基线下缘垂直地测量到波的底端。
Measurement of P wave terminal forcein V1 lead (PTFV1) (Fig.1-15)
PTFV1 represents the P wave terminal force in V1 lead, which is the product of the negative P wave depth (mm) and the width (s). Add a negative sign in the result of product, and the unit is -mm·s.The absolute value of PTFV1 is increased when it’s abnormal.
V1导联P波终末电势(PTFV1)测量(图1-15)
PTFV1表示V1导联P波终末电势,是负向P波深度(mm)和宽度(s)的乘积。在乘积前加负号,单位为-mm·s。PTFV1异常,绝对值增大。

Fig.1-15 Measurement of PTFV1
图1-15 PTFV1的测量方法
A: Solution of measurement when P wave starting point is on the same level with P-R segment.
B, C: Solution of measurement when the P-R segment shifts upward or downward.
A为P波起始部与P-R段在同一水平时的测量法;B、C分别为P-R段上移与下移时测量方法。
QRS, ST-T measurements
QRS origin is used as the reference when measuring QRS complex, J-point, ST-segment,T wave, and U wave amplitude. If the QRS origin is an oblique segment (affected by delta wave,atrial repolarization wave, etc.), QRS complex origin point should be used as reference. The reasons were as follows: ⅰ. It should not be changed when heart rate or other conditions changing,otherwise it will increase measurement differences. ⅱ. There is better reproducibility when using QRS starting point as reference. ⅲ. The concept that T-P segment represents zero potential is a misunderstanding. ⅳ. QRS origin has been used as reference for treadmill electrocardiogram and the body surface measurement methods for many years, so the concept that T-P segment and the P-R segment are the baseline references should be abolished.
The forward R (R′) was measured vertically from the upper edge of the QRS to the peak of R wave, and the negative waves (Q, S, QS) are measured vertically from the lower edge of the QRS starting edge to the bottom of R wave.
There is no single standard for measuring ST segment. When the ST segment horizontally declined, the amplitude of ST segment should be the distance between the ST segment level and QRS originvertically. When the shift of ST segment was upward or downward, the ST segment should be measured at 40, 60 or 80ms after the point J. ST40, ST60, ST80 represent the degree and shape of ST segment shift.
The forward T wave is measured perpendicularly from the upper edge of the reference level to the peak of T wave, and the negative wave (Q,S,QS) is measured vertically from the lower edge of the reference horizontal line to the bottom.
Measurement of U wave is the same as T wave.
QRS、ST-T测量
QRS波群、J点、ST段、T波和U波振幅的测量统一采用QRS起始水平作为参考水平。如果QRS起始部为一斜段(受预激波、心房复极波的影响等),以QRS波群起点作为测量参考点。其理由是:①作为一个定义,不应该使测量程序因心率或其他条件变化而改变,否则将增加心电图的测量差异性;②以QRS起始部为参考水平,重复性好;③认为T-P段代表零电位是一种误解;④负荷试验心电图以及体表标测法多年来一直以QRS起始部作为参考水平,以T-P段和P-R段作为基线参考水平应废除。
测量R波时,若为正相波,则自QRS起始部上缘垂直地测量到R(R′)波顶点,若为负向波(Q、S、QS),则自QRS起始部下缘垂直地测量到波的底端。
测量ST段尚无统一标准。ST段呈水平型下降时,测量ST段水平部与QRS起始部的垂直距离,ST段呈上斜型或下斜型移位时,在J点后40、60或80ms处测量。ST40、ST60、ST80即ST段移位的程度和形态。
T波的测量,正向T波自参考水平上缘垂直地测量至波顶点,负向T波自参考水平线下缘垂直地测量到波底端。
U波的测量与T波相同。

Fig.1-16 Measurement of ST segment shift
图1-16 ST段移位的测量
A: Measured amplitude of ST segment when it is elevated. B: Measured amplitude of ST segment when it declined. C: When heart rate increased,T wave and P wave overlapped, T-P segment disappeared, PR segment downward shifted, J point depressed, ST segment upward shifted. The line between the origins of two continuous Q wave was regarded as an equipotential line. Thus the decline degree of J point and ST segment could be measured based on this line.
A:ST段抬高的测量;B:ST段下降的测量;C:心率快时,T波与P波重叠,T-P段消失,PR段下斜,J点降低,ST段斜向上,此时两个连续Q波起点间的连线作为等电线用于测定J点和ST段下降的程度。